本站资源全部免费,回复即可查看下载地址!
您需要 登录 才可以下载或查看,没有帐号?立即注册

x
CSS中定位介绍#- position属性在英文单词中表示位置的意思,在CSS中主要作用设置元素的定位。
- CSS中一共有3种定位如下
属性值描述
fixed设置固定定位。
relative设置相对定位。
absolute设置绝对定位。
固定定位实践#- 在实践固定定位之前我们先看看代码结构是什么样子的呢。
代码块
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color:springgreen;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="box"></h1>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
结果图
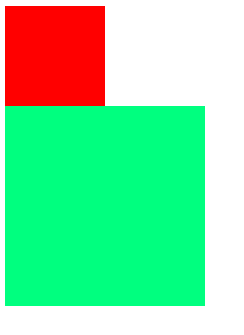
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
position:fixed;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color:springgreen;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="box"></h1>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
结果图
- 固定定位特点分析如下:
- 固定定位,它是相对于浏览器窗口进行设置定位,不管页面如果滚动,固定定位的元素位置不会受到任何影响。
- 固定定位的元素特点:它已经脱离了标准文档流。
- 固定定位的元素特点:它的层级比标准文档流的元素要高,所以我们给h1标签设置了固定定位会压盖到div标签。
- 固定定位的元素特点:h1标签在div标签之上,所以固定定位的元素已经不再占用任何空间。
相对定位实践#- 在实践相对定位之前我们先看看代码结构是什么样子的呢。
代码块
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图

[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
position: relative;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图

注意:在我们没有给相对定位设置坐标位置,它是不会有任何移动的。
- 笔者给class属性值为div2元素设置定位坐标实践。
代码块
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图
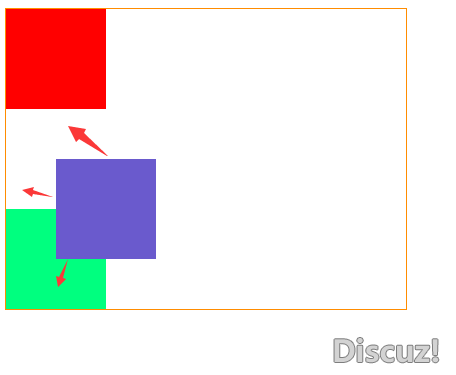
- 相对定位特点分析如下:
- 相对定位的元素它没有脱离标准文档流。
- 相对定位的元素如果没有设置坐标它会在原地位置。
- 相对定位的元素设置了坐标位置,它会根据原来的位置开始计算移动的位置。
- 相对定位的元素它比标准文档流的元素层级要高,会覆盖标准文档流中的元素。
- 相对定位的元素它可以设置为负数。
绝对定位实践#- 在实践绝对定位之前我们先看看代码结构是什么样子的呢。
代码块
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图

[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
position:absolute;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图

注意:绝对定位已经脱离了标准文档流。
- 笔者给class属性值为div2元素设置定位坐标实践,为了让读者有一个直观的印象我给最外层的div元素设置了居中对齐。
代码块
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
margin: 0px auto;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
position:absolute;
left:0px ;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图

注意:绝对定位元素为什么会出现在浏览器左边缘呢,绝对定位移动原理:绝对定位的元素它会寻找父元素是否有定位,如果有定位它会根据父元素进行定位,如果父元素没有设置定位,它会在找父元素的父元素是否有定位,以此类推直到body元素就停止了,因为body元素就是浏览器的位置,说了这么多笔者给新学者一个直观的印象,那咱们就实践见真招。
代码块
[HTML] 纯文本查看 复制代码 <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>定位</title>
<style>
.box{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid darkorange;
margin: 0px auto;
position: relative;
}
.box div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.div1{
background-color: red;
}
.div2{
background-color: slateblue;
position:absolute;
right:0px ;
}
.div3{
background-color: springgreen;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
结果图
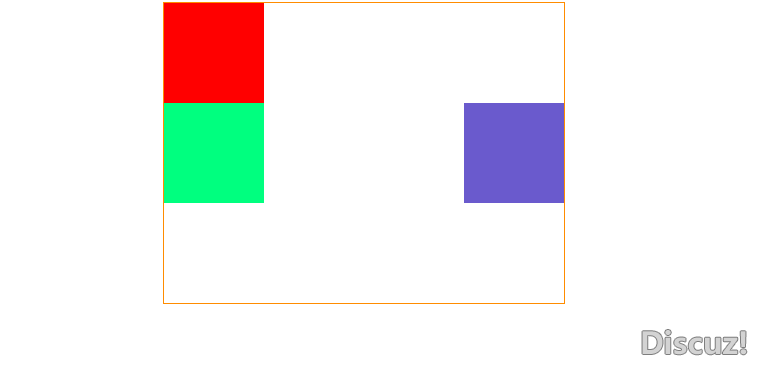
注意:现在笔者给绝对定位坐标更换成了向右定位,父元素设置了一个相对定位,在这里就不多进行实践了,如果定位的父元素的父元素也就是爷爷的元素,父元素和爷爷元素同时都设置了定位,该元素会根据父元素决定定位而不是爷爷元素。
- 绝对定位特点分析如下:
- 绝对定位元素它已经脱离了标准文档流。
- 绝对定位元素它会覆盖掉标准文档流的元素。
- 绝对定位元素它已经不再占用任何空间了。
- 绝对定位元素它根据父元素之祖先元素之间是否有定位,如果有根据最近元素进行设置定位的位置,如果没有根据body元素进行定位。
- 绝对定位元素的父元素可以是用任何定位包括绝对定位,笔者建议是用相对定位,一般相对定位是配合着绝对定位使用的
|